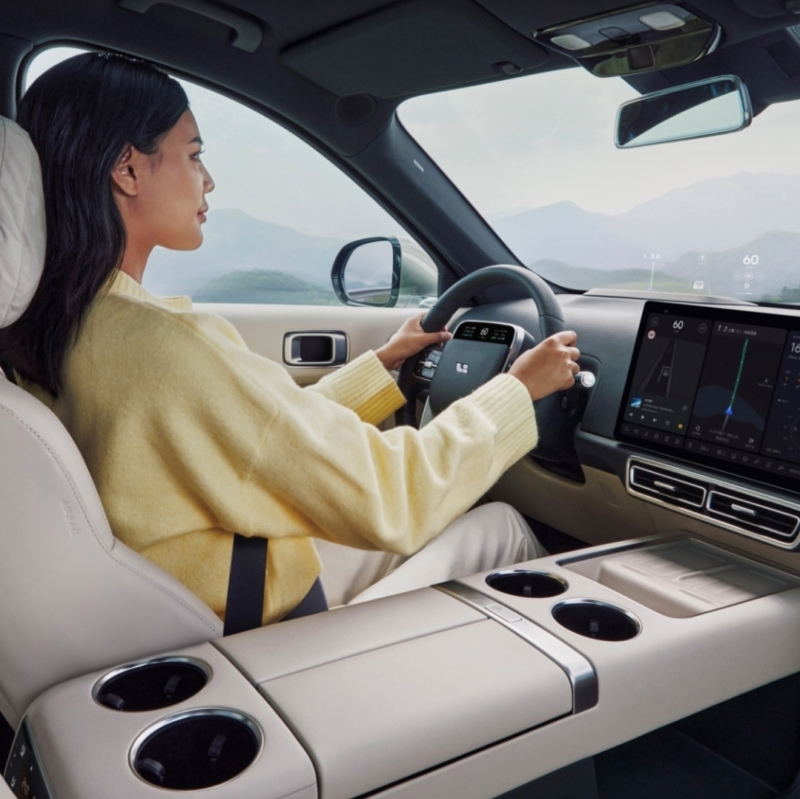
The Chinese MIIT intends to require physical control mechanisms for functions such as turning turn signals on/off, raising/lowering windows, and activating advanced driving assistance system. This new requirement is expected to be mandatory for only newly manufactured vehicles starting July 1, 2026.
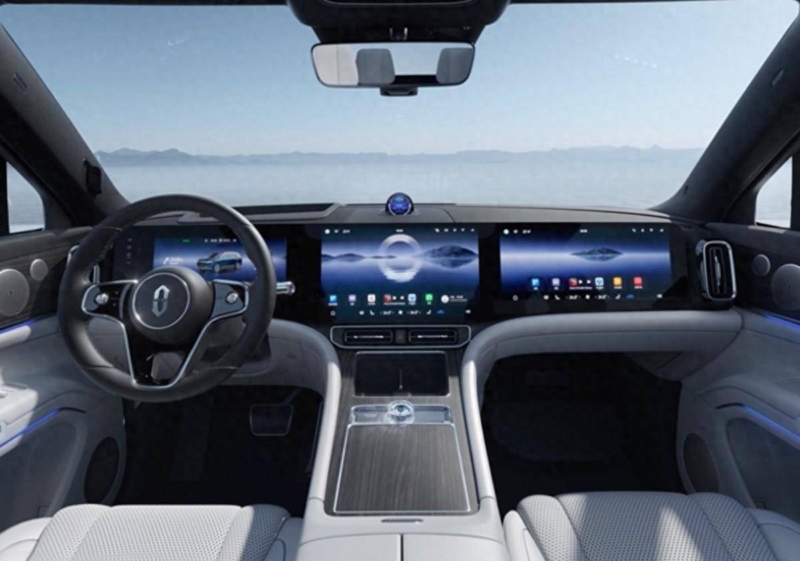


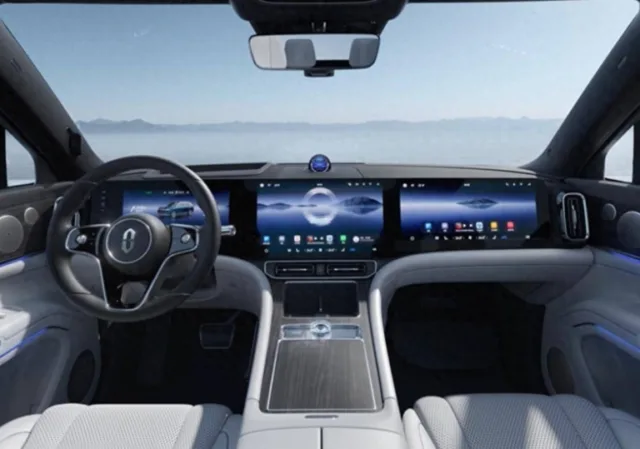
In recent years, a theme among Chinese new energy vehicles is minimalistic cockpit design, with one of its characteristics being minimal presence of physical control buttons. Instead, a large central control screen houses most of the vehicle functions, and sometimes paired with co-pilot entertainment screen. This ubiquitous design was described by Geely’s VP as the “Chinese automotive industry is plagued by a trend of blindly following trends.”
As a revision to the existing national standard GB4094—2016 “Marking of Automotive Control Components, Indicators, and Signaling Devices”, the update adds new types and technical requirements for physical control components, ensuring that key control components are accessible, usable, and largely blind-operable during driving, without overly relying on visual input and reduce distractions caused by display screens.
This revision started in 2023, involving major automotive manufacturers and testing institutions, including China Automotive Technology and Research Center, Geely, FAW-Volkswagen, BYD, and Great Wall Motor. A draft for public comment has been completed and will be released soon, which specifically includes the following functions:
- Lighting: Turn signals, hazard warning lights (double flashers), horn
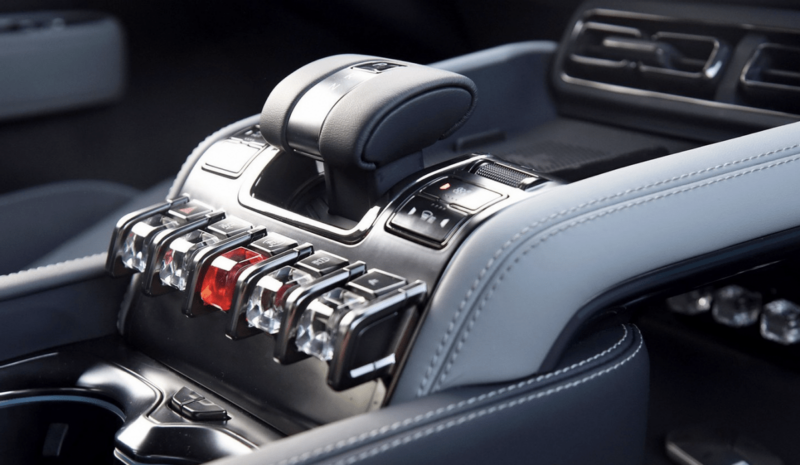
- Gear shifting: P/R/N/D (screen-only shifting is prohibited)
- Driver assistance: Activation switch for the advanced driver assistance system
- Safety/emergency: Windshield wipers, defroster/defogger, power windows, Child/Accident Emergency Call System (AECS), and electric vehicle power off switch
Other detailed requirements for physical controls were also specified such as dimensions (effective operating area ≥ 10 mm x 10 mm), usability (fixed position, blind operation, haptic/auditory feedback), and reliability (basic functions remain available when the vehicle system crashes/power is lost).
Source: Chinese MIIT
Follow us for ev updates